You can create custom export templates using Handlebars syntax to export ReqView projects into HTML, CSV, JSON, XML or any other structured text format fitting your specific requirements for data layout and visual style.
If you need help we can tailor your reports for you, see Custom Services > Advanced Reports.
Custom Export
To export a text file using a custom template, click File, mouseover Export and click Custom Template. In the Export Using Custom Template dialog, choose exported documents and other options. After confirmation of the dialog, select a destination for storing the exported files.
The exported files are named according to the project or document ID with the same extension as the template file (for example, SRS.html).
Note: In the WebApp, the exported files are saved in the browser download folder.
Export Options
Documents:
Select exported documents:
- Current document — export the current document only.
- Open documents — export all open documents from the main project or loaded linked projects.
- All documents from the main project — export all documents from the main project.
- All documents from loaded projects — export all documents from the main project or loaded linked projects.
Table View:
Select a table view defining which attributes or template columns will be exported:
- Current or default view — export open documents using the current table view and closed documents using the default view.
- <table view> — export documents using the selected table view. Documents without the selected table view are exported using the last used or the default table view.
For more information see Table Views.
Layout:
Choose a custom export template file specifying the layout and styling of exported data.
Options:
- Merge documents into a single file — if set then all exported documents will be merged into a single HTML file, otherwise a separate file will be created for each exported document (for Open documents and All documents options).
- Merge displayed custom attributes — if set then columns displaying custom attributes will be compacted into a single column.
- Ignore filter — if the exported table view is filtered then this options controls if the filter is preserved or ignored.
- Ignore sorting — if the exported table view is sorted by a selected column then this option controls if the sort order is preserved or ignored.
- Ignore links to invisible objects — if set then do not include links from / to document objects which are not visible in the exported file.
- Preserve section folding — if set then content of collapsed sections will be ignored.
- Explore and load linked projects — if set then indirectly linked projects will be explored and loaded to display additional traceability links, see Manage Linked Project.
- Add custom export parameters – pass custom export parameters to your custom template from a selected JSON file, see helper
exportParambelow.
Export Configuration
You can export documents to text files easily using a shared export configuration storing all export options, see Export Configurations.
Export CLI
You can export documents to text files using reqview export custom command, see Command Line > Export Documents.
Exported Data Model
The exported data model describes the project, documents and traceability links. ReqView passed the data model to the selected export template which describes how to convert the data model into a text output by means of a text markup and export helpers.
Documents
Exported documents contains the following properties at the top level:
- docId — document identifier
- createdOn — date of document creation
- createdBy — document author record
- name
- company
- lastChangedOn — date of the last modification
- lastChangedBy — last modification author record
- name
- company
- tableView — name of the table view used for export
- filter — collection of filtering criterions
- criterion — filtering criterion definition
- sort — document sort record
- attribute — ID of the attributed used for sorting
- descending — true if sort is descending
- columns — collection of column records
- id — the given column identifier, for example “description” or a custom attribute identifier
- icon — icon name for the given column
- userDefined — true if the given column is a custom attribute
- sortAsc — true if the given column is sorted with ascending order
- sortDesc — true if the given column is sorted with descending order
- document objects — collection of document objects, see helper
eachDocumentObject
You can iterate exported documents by helper eachDocument or output a given document by helper withDocument.
Document Objects
Exported document objects contains information about attributes, template columns, file attachments, discussion, and traceability links:
- id — unique object identifier within the document
- guid — globally unique object identifier
- heading — section heading
- text — text description
- deleted — flag set to true if the object is marked as deleted
- level — section level of the object
- parent — unique identifier of the parent object within the document
- discussion — collection of comments, see helper
arrayfor an example- date — date of the comment
- author — author of the comment
- name
- company
- comment — text of the comment
- custom attributes — to output the attribute value, use
{{<attributeId>}}expression, oreachDisplayedCustomAttributeorattributeValuehelpers - template columns — use helper
eachColumn - file attachments — user helper
eachAttachment - traceability links — use helpers
eachInlinkType/eachOutlinkTypeandeachInlinkWith/eachOutlinkWith
To access these document object properties, use {{<property>}} expression. For instance, {{id}} outputs the document object ID, {{heading}} outputs the section heading, and {{status}} outputs the value of custom attribute status.
To iterate exported document objects, use helper eachDocumentObject.
Export Templates
ReqView export templates use Handlebars syntax to describe conversion of the project data into a structured text format, such as HTML, CSV, JSON or XML.
Template Expressions
You can customize export templates using expressions or template helpers. Handlebars expressions are some contents enclosed by double curly braces – e.g. {{<expression>}}. Expressions in this form produce HTML escaped output. If you don’t want to escape the expression value, use the “triple-stash” form: {{{<expression>}}}.
For example, {{text}} outputs object text description with HTML escaped tags <p>User shall …</p> while {{{text}}} outputs the object text description with the original HTML tags <p>User shall …</p>.
Whitespace (for example, line endings) in the template is preserved into the output text. If you want to trim whitespace from either side use a tilde (~) by the braces, see Handlebars: Whitespace Control. For example, {{~expression}} removes all whitespace before the expression up to the first handlebars expression or non-whitespace character.
Note: We strongly recommend using ReqView identifiers for projects, documents, attributes and traceability link types without any white space (e.g. using camel case) to simplify their handling in export templates. You may need to wrap identifiers in [] brackets if it contains a white space or another not allowed character, see Handlebars: Literal Segments.
Template Helpers
Handlebars define a rich set of built-in template helpers allowing you to conveniently iterate through an object structure and output object properties using expressions. The most useful of them is the predefined conditional block helper allowing you to render block content based on the result of the given expression:
… … To pass values to a helper with parameters, list the parameters after the helper name:
Unlike the if helper mentioned above, most custom block helpers (usually named each… or with…) change the current evaluation context. Sometimes it is necessary to reach into parent context when nesting such helpers – this is done using the {{../<property>}} syntax, similar to how directory paths work.
Template Inline Partials
You can reuse template code through Handlebars inline partials. For example:
- HTML Tables — use inline partials to reuse template code.
- HTML Traceability Reports — use inline partials to recursively iterate the traceability graph and output a traceability coverage across several levels.
- HTML Progress Reports — use inline partials to recursively iterate document structure and output aggregated progress for each section.
Export Helpers
You can use also the following ReqView template helpers that simplify access to the exported data model.
Project Helpers: eachDocument • eachOpenDocument • exportOption • exportParam • projectId • withDocument
Document Helpers: docName • eachDocumentObject • isRTL
Document Object Helpers: attributeValue • countInlinks/countOutlinks • docObjId • eachAttachment • eachChild • eachInlinkType/eachOutlinkType • eachInlinkWith/eachOutlinkWith • eachOriginInlink • hasChild • hasInlinks/hasOutlinks • hasOriginInlink/hasOriginOutlink • ifHasInlinks/ifHasOutlinks • indentation • isSection • lastChangedOn • section • sectionNumber • shortDescription • withOriginOutlink • withParent • withParentLink
Attachment Helpers: imageSize
Link Helpers: eachLink • hyperlink • ifSuspect • linkTypeName
Column Helpers: attributeColumnType • attributeColumnValue • columnAttributeValue • columnId • columnName • columnProperty • eachColumn • eachDisplayedCustomAttribute • isAttributeColumn • isColumn • isTemplateColumn • templateColumnValue
Formatting Helpers: formatDate • formatDateTime •formatJSONString • formatPrefixedXHTML • formatString • formatTime • formatURIComponent • formatXHTML
CSV Output Helpers: csvSeparator • formatAttributeCSVColumn • formatBlockCSVColumn • formatCSVColumn • formatCustomAttributeCSVColumn • formatSystemAttributeCSVColumn
Expression Helpers: and • cond • decr • eval • get • ifEqual • incr • join • not • or • set • var
Array & Map Helpers: array • clear • deleteElement • eachOfMap • getElement • includes • map • pop • push • setElement • size • sort
Search & Replace Helpers: replaceRegexp • replaceString • searchRegexp • searchString
Other Helpers: debug • let • repeat • user
Project Helpers
projectId
Syntax: {{projectId}}
Description: Outputs the project ID for the exported document.
eachDocument
Syntax: {{#eachDocument [separator=<string>]}} … {{/eachDocument}}
Description: Iterates all exported documents. You can optionally specify a custom separator string by separator parameter.
Example: Export all documents to a single HTML file with book layout. Document objects having attribute heading set are exported using numbered HTML heading tags. Document objects having attribute text set are exported as HTML paragraphs prefixed by document object ID.
<h1></h1> <hr> <span class="id">[]</span> Note: If you wish to output only specific documents, have a different layout for each document or change the order of documents, use multiple template blocks within the template file wrapped by withDocument helper.
eachOpenDocument
Syntax: {{#eachOpenDocument [separator=<string>]}} … {{/eachOpenDocument}}
Description: Iterates all open documents when exporting into a single file. You can optionally specify a custom separator string by separator parameter.
Example: Output list of all open document names separated by a comma:
eachDocument helper instead.withDocument
Syntax: {{#withDocument <docId>}} … {{/withDocument}}
Description: Sets the child context to the document with the given ID when exporting into a single file.
Example: Output document name for ID "NEEDS":
exportOption
Syntax: {{exportOption <option>}}
Description:
{{exportOption "mergeDocuments"}}— outputs a non-empty string if export option Export into a single file is checked{{exportOption "exportSection"}}— outputs the name of a MS Word DOCX export section, see Export DOCX > Export Sections
exportParam
Syntax: {{exportParam <propertyPath>}}
Description: Gets a value from the custom export parameters JSON file provided in the Export Options dialog or via CLI. The propertyPath argument can refer to any top-level property or a property in nested objects using the dot path notation.
Example Params File:
{ "textParam": "foobar", "number": 12345, "boolean": true, "nested": { "abc": "foo", "deep": { "def": "bar" } }, "array": [1, 2, "baz"]}Example: Get value of textParam property (“foobar“):
Example: Get value of deeply nested def property (“bar“):
Example: Get value of array property at index 2 (“baz“):
Example: Iterate over the array property using the Handlebars built-in #each helper:
<ul> <li></li></ul>Example: Output the SVN revision of a ReqView project to HTML.
-
Run the following bash command in a ReqView Project Folder to store its SVN revision into a JSON file:
$ echo "{ \"svnRevision\": \"`svn info --show-item revision`\"}" > exportParamFile.json -
Create a custom HTML export template with the following snippet to output the SVN revision stored in the JSON file:
<p><strong>SVN revision</strong>: </p> -
Export the project to HTML using the ReqView CLI
$ reqview export custom -p <project_folder> -t <template> -j exportParamFile.json -o <output_folder>
Document Helpers
docName
Syntax: {{docName [docId=<string>]}}
Description: Outputs document name of the current document or a document with the given document ID.
Example: Output name of SRS document:
eachDocumentObject
Syntax: {{#eachDocumentObject [separator=<string>]}} … {{/eachDocumentObject}}
Description: Iterates all document objects in the exported document. You can optionally specify a custom separator string by separator parameter.
Example: Output list of document object IDs separated by a comma:
isRTL
Syntax: {{isRTL}}
Description: Checks if the default text direction for the current document is RTL (right-to-left).
Example: Add appropriate dir attribute and text-align style to a heading tag containing the document name:
<h1 dir="rtl" style="text-align: start;"></h1>Document Object Helpers
docObjId
Syntax: {{docObjId}}
Description: Outputs the object ID prefixed by the document ID.
Example: Display links as object IDs (strip document IDs using a regular expression).
shortDescription
Syntax: {{shortDescription [attribute=<attrId>] [maxLength=<number>]}}
Description: Outputs short text description (with stripped HTML) of the object attribute given by parameter attribute. If attribute parameter is not present then it outputs value of system attribute heading / text. You can specify the maximum number of characters by optional maxLength parameter.
Example: Output object description from heading and text attributes shortened to 80 characters:
sectionNumber
Syntax: {{sectionNumber}}
Description: Outputs section number as a plain text, for example “1.2.3”.
isSection
Syntax: {{isSection}}
Description: Returns true if the current document object has section, i.e., helper sectionNumber returns a non-empty value.
Example:
Section: section
Syntax: {{#section [numbering=<bool>] [shiftLevel=<number>] [tocMember=<number>]}} … {{/section}}
Description: Generates a HTML heading (<h1>, <h2>, ... tags) for the current section. If its optional parameter numbering is true, then it also outputs the section number. Optional parameter shiftLevel denotes the number of heading level shift. Optional parameter tocMember denotes the maximum section level which will be present in a table of content in the exported PDF document.
Note: Section headings below level 6 will be exported using the <h6> HTML tag.
Example: Output the section number followed by section heading and shift level by 1 to use <h2> tag for the top level:
indentation
Syntax: {{indentation <number>}}
Description: Calculates indentation space from the object level in the document hierarchy (if filter is not active). The argument provides the number of pixels per level.
Example: Indent a div HTML tag by 10px per level:
<div style="padding-left:"></div>Example: Same as example above but manually indent based on object level in the document hierarchy (works independently on filter state):
<div style="padding-left:px"></div>attributeValue
Syntax: {{attributeValue <attrId> [format="string"|"xhtml"] [inherit=true]}}
Description: Formats the value of the given document object attribute. You can optionally provide output format (default is "xhtml") and enable inheritance of attribute value from its nearest parent if it is not set.
Note: Use this helpers to output labels of enumeration attributes values because {{<attributeId}} outputs the enumeration key(s).
Example: Output the label (for example, “Implemented”) of the value stored in the custom enumeration attribute status:
Example: Output the value of the attribute text converted to a plain string:
Tip: To check if an enumeration attribute value matches a string, use the includes helper.
lastChangedOn
Syntax: {{lastChangedOn [attrId]}}
Description: Returns the date and time of the last change of any of the document object’s attributes, or of a specified attribute when attrId is present.
Example: Output the date and time of the last attribute change of a document object:
Example: Mark an object whose status attribute was last changed on or after 18 June 2019:
<b>Changed</b>eachChild
Syntax: {{#eachChild [separator=<string>]}} … {{/eachChild}}
Description: Iterates the immediate children of the current document object.
Example: Output a comma separated list of child object IDs:
Example: Output a hierarchy tree of all descendant objects in a nested bullet list:
<ul> <li> </li> </ul>
hasChild
Syntax: {{hasChild}}
Description: Checks if the current document object has any child.
Example: Output IDs of all child objects:
<span></span> eachAttachment
Syntax: {{#eachAttachment}} … {{/eachAttachment}}
Description: Iterates the attachments of the current document object. The child context contains the following properties:
- name — attachment name
- data — attachment data as base64 string
- href — relative URL to the attachment file
- isImage — flag if attachment is an image type
Example:
<img src=""> <div><em>Image attachment:</em> </div> <div><em>File attachment:</em> </div> hasInlinks / hasOutlinks
Syntax: {{hasInlinks [linkTypeId]}}
Description: Returns true if the current document object has an inlink (resp. outlink). You can optionally provide a link type ID.
Example:
<span>OK.</span> <span>Missing satisfaction link!</span>ifHasInlinks / ifHasOutlinks
Syntax: {{#ifHasInlinks <linkTypeId>}} … {{/ifHasInlinks}}
Description: Outputs the given block if the current document object has an inlink (resp. outlink) of the given link type ID. An else block can be optionally provided.
Example:
<span>OK.</span> <span>Missing satisfaction link!</span>if, hasInLinks / hasOutLinks helpers instead.countInlinks / countOutlinks
Syntax: {{countInlinks [linkTypeId]}}
Description: Returns the number of inlinks (resp. outlinks) of the current document object. You can optionally provide a link type ID.
Example:
eachInlinkType / eachOutlinkType
Syntax: {{#eachInlinkType}} … {{/eachInlinkType}}
Description: Iterates incoming (resp. outgoing) traceability link types for the current document object.
Example:
<div>:</div> <div> </div> eachInlinkWith / eachOutlinkWith
Syntax: {{#eachInlinkWith type=<typeId> [separator=<string>]}} … {{/eachInlinkWith}}
Description: Iterates incoming (resp. outgoing) traceability links of type given by type parameter. You can optionally specify a custom separator string by separator parameter. Links are sorted the same way as in the displayed table view.
Example:
<span></span>withParent
Syntax: {{#withParent}} … {{/withParent}}
Description: Renders the given block with the parent document object context. The parent context is accessed even if the parent or the link to it is not visible.
Example: Get the ID of the object’s parent:
<div><em>Parent ID:</em> </div>Example: Get IDs of parents of linked objects:
<div><em>Parent ID of linked object:</em> </div> withParentLink
Syntax: {{#withParentLink}} … {{/withParentLink}}
Description: Renders the given block with the parent document object context if parent links are displayed (Edit > Preferences > Show parent links).
Example:
<div><em>Parent:</em> </div>hasOriginInlink / hasOriginOutlink
Syntax: {{hasOriginInlink}}
Description: Returns true if origin links are displayed (Edit > Preferences > Show origin and inherited links) and if the given document object has an incoming (resp. outgoing) origin link.
Example:
Has CopiesIs CopyeachOriginInlink
Syntax: {{#eachOriginInlink}} … {{/eachOriginInlink}}
Description: If origin links are displayed (Edit > Preferences > Show origin and inherited links), it iterates object’s copies.
Example:
<div><em>Copy:</em> </div>withOriginOutlink
Syntax: {{#withOriginOutlink}} … {{/withOriginOutlink}}
Description: If origin links are displayed (Edit > Preferences > Show origin and inherited links) and the given document object is a copy, it sets child context to the original object.
Example:
<div><em>Origin:</em> </div>Attachment Helpers
imageSize
Syntax: {{imageSize [maxWidth=<number>] [maxHeight=<number>]}}
Description: Outputs width and height attributes of <img> HTML tag describing current attachment image size. You can optionally provide maxWidth or maxHeight parameters to rescale the image.
Example:
<img alt="" src="" />Link Helpers
linkTypeName
Syntax: {{linkTypeName}}
Description: Outputs the name string of the current link type, for example “Satisfies”.
eachLink
Syntax: {{#eachInlink}} … {{/eachInlink}}
Description: Iterates traceability links of the current traceability link type for the current document object. Links are sorted the same way as in the displayed table view.
Example:
<div>:</div> <div> </div> hyperlink
Syntax: {{#hyperlink}} … {{/hyperlink}}
Description: If the link source (resp. target) document is included in the HTML export, then it creates an HTML a tag around the inner block pointing to the link source (resp. target) object.
Example:
ifSuspect
Syntax: {{#ifSuspect}} … {{/ifSuspect}}
Description: Outputs the given block if the link is suspect.
Example:
!Column Helpers
eachColumn
Syntax: {{#eachColumn}} … {{/eachColumn}}
Description: Iterates displayed columns of the table view.
eachDisplayedCustomAttribute
Syntax: {{#eachDisplayedCustomAttribute}} … {{/eachDisplayedCustomAttribute}}
Description: Iterates attributes displayed in the Custom Attributes column and sets context id, name, value, and rawValue properties to attribute ID, name, and formatted (resp. unformatted) value.
Example:
<div class="attribute"> <span>:</span> <span></span> </div> columnId
Syntax: {{columnId}}
Description: Outputs column ID, for example “description”.
Example:
<tr> <th></th></tr>columnName
Syntax: {{columnName [<colId>]}}
Description: Outputs column name of the current column in eachColumn context or name of the given column if colId argument is provided.
Example:
<tr> <th><strong>▲▼</strong></th></tr>columnProperty
Syntax: {{columnProperty <propertyName>}}
Description: Gets a column property by its name.
Example: Output values in all columns:
<tr> <td></td> <td></td> </tr>isColumn
Syntax: {{isColumn <colId>}}
Description: Returns true if the current column matches the given column ID.
Example:
<tr> <td><a id=""></a></td> </tr>if, eval, and columnId helpers instead.isAttributeColumn
Syntax: {{isAttributeColumn [type="custom"|"system"]}}
Description: Returns true if the current column is an attribute column. You can optionally check if it is a custom or a system attribute.
isTemplateColumn
Syntax: {{isTemplateColumn}}
Description: Returns true if the current column is a template column.
attributeColumnValue
Syntax: {{attributeColumnValue [format="string"|"xhtml"]}}
Description: Outputs value of the attribute corresponding to the current column. You can optionally provide output format (default is "xhtml").
Example: Output the value of the current attribute in XHTML format:
Example: Output the value of the current attribute converted to a plain string:
columnAttributeValue
Syntax: {{columnAttributeValue [format="string"|"xhtml"]}}
Description: Outputs value of the attribute corresponding to the current column. You can optionally provide output format (default is "xhtml").
Example: Output the value of the current attribute in XHTML format:
Example: Output the value of the current attribute converted to a plain string:
attributeColumnValue helpers instead.attributeColumnType
Syntax: {{attributeColumnType}}
Description: Outputs type of the attribute.
Example: Output the value of the current attribute in proper format with respect to its type:
templateColumnValue
Syntax: {{templateColumnValue <columnName>}}
Description: Outputs value of the template column with the given ID or label.
Note: Scope of variables declared inside the template column is limited to this helper.
Example:
<tr> <td></td> </tr>Formatting Helpers
formatString
Syntax: {{formatString <string> [maxLength=<number>] [newlines=<bool>] [case="firstLower"|"allLower"|"firstUpper"|"allUpper"] [locale=<string>]}}
Description: Formats a value as a string (strips HTML tags). You can optionally provide the maxLength parameter with a maximum number of string characters. If the optional parameter newlines is true, then all p, li and br end tags are replaced by line feed (\n, 0x0A) characters. The optional case parameter allows case conversion of the first or all characters in the string to lower or upper case. To get the correct lower or upper case of language-specific characters, you can optionally use a IETF BCP 47 language tag as the locale argument.
Example: Strip HTML from the text attribute and limit the result’s length to 20 characters:
Example: Convert the first letter of “istanbul” to upper case, passing in the Turkish locale to get the correct output “İstanbul”:
formatJSONString
Syntax: {{formatJSONString <string>}}
Description: Formats a string value as a JSON string.
formatXHTML
Syntax: {{formatXHTML <string> [paragraphClass=<string>] [charClass=<string>]}}
Description: Formats a value as XHTML. You can optionally provide paragraphClass parameter with a paragraph class name for p or div tags or charClass parameter with an inline class name for span tag.
Example:
<div><b>Description</b>:</div><div></div>formatPrefixedXHTML
Syntax: {{#formatPrefixedXHTML <string> [paragraphClass=<string>] [charClass=<string>]}} … {{/formatPrefixedXHTML}}
Description: Formats a value as XHTML with a custom prefix given by the child block. You can optionally provide paragraphClass parameter with a paragraph class name for p or div tags or charClass parameter with an inline class name for span tag.
Example: Output value of text attribute of the current document object. If heading attribute is not set, then insert the document object ID at the start of the first paragraph.
<span>[]</span>formatDateTime
Syntax: {{formatDateTime [<date>] [format=<format>]}}
Description: Formats a given date/time value (ISO 8601) or the current date and time if the value is not provided.
Use format parameter to specify a custom date/time format according to ECMA-376 — Office Open XML file formats — Date and time formatting standard. ReqView supports the following formatting options:
d— formats the day of the week or day of the month as a number without a leading zero for single-digit days,dd— formats the day of the month as a two-digit number with a leading zero for single-digit days,M— formats the month as a number without a leading zero for single-digit months,MM— formats the month as a number with a leading zero for single-digit months,yy— formats the year as a 2-digit number,yyyy— formats the year as a 4-digit number,H— formats the hour on a 24-hour clock without a leading zero for single-digit hours,HH— formats the hour on a 24-hour clock with a leading zero for single-digit hours,h— formats the hour on a 12-hour clock without a leading zero for single-digit hours,hh— formats the hour on a 12-hour clock with a leading zero for single-digit hours,m— formats the minutes without a leading zero for single-digit minutes,mm— formats the minutes with a leading zero for single-digit minutes,s— formats the seconds without a leading zero for single-digit minutes,ss— formats the seconds as a two-digit number with a leading zero for single-digit seconds,am/pm— formats the uppercase 12-hour clock indicator.
The default is ISO date time format “yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm”, for example “2015-09-01 16:00”.
Example: Output the value of custom attribute createdOn in the common European format, for example “13.8.2015 14:20”.
formatDate
Syntax: {{formatDate [<date>]}}
Description: Formats a date value (ISO 8601) as “yyyy-MM-dd”, for example “2015-09-01”. Outputs the current date if no parameter is provided.
formatTime
Syntax: {{formatTime [<date>]}}
Description: Formats a time value (ISO 8601) as “hh:mm”, for example “16:00”. Outputs the current time if no parameter is provided.
formatURIComponent
Syntax: {{formatURIComponent <string>}}
Description: Formats a URI by escaping reserved characters their UTF-8 encoding.
CSV Output Helpers
csvSeparator
Syntax: {{csvSeparator}}
Description: Outputs CSV separator set in the Preferences dialog.
formatCSVColumn
Syntax: {{formatCSVColumn <value>}}
Description: Formats given value as a CSV column (escapes double quotes, line ends, etc.).
Example:
formatBlockCSVColumn
Syntax: {{#formatBlockCSVColumn}} … {{/formatBlockCSVColumn}}
Description: Formats given value as a CSV column (escapes double quotes, line ends, etc.).
Example: Output IDs of all document objects linked to the current document object with verification link type.
formatAttributeCSVColumn
Syntax: {{formatAttributeCSVColumn <attrId>}}
Description: Formats value of the given document object attribute as a CSV column.
Example: Output CSV value of heading system attribute:
formatSystemAttributeCSVColumn
Syntax: {{formatSystemAttributeCSVColumn <attrId>}}
Description: Formats value of the given document object system attribute as a CSV column.
formatAttributeCSVColumn instead.formatCustomAttributeCSVColumn
Syntax: {{formatCustomAttributeCSVColumn <attrId>}}
Description: Formats value of the given document object custom attribute as a CSV column.
formatAttributeCSVColumn instead.Expressions Helpers
Binary Operators
eval
Syntax: {{eval <lvalue> <operator> <rvalue>}}
Description: Evaluates an expression given by three arguments — left value, binary operator and right value. The binary operator can be + (add), - (subtract),
* (multiply), / (divide), == (equal), != (not equal), < (less), <= (less or equal), > (greater), >= (greater or equal), && (logical and), || (logical or).
Example: Multiply value of severity, probability and detectability attributes in project risks document:
Example: Set value of string variable z as concatenation of string variables x and y.
Note: You concatenate strings more conveniently using helper join.
Example: Highlight values of a numeric attribute rpn greater than 100:
<div {{#if (eval rpn ">" 100)}}style="font-weight:bold; background-color:red;"{{/if}}> {{rpn}}</div>Example: Display warning if document object type attribute is set to “Req” and the document object has no incoming link:
<div><b>Warning:</b> Missing incoming link!</div> Example: Convert string values to integer, e.g. for integer comparison tests.
stringCompare:</br> stringCompare:</br> Logical Expressions
and
Syntax: {{and <value 1> <value 2> … }}
Description: Evaluates logical and for two or more given arguments.
Example: Display names of all document object attachments. For each image attachments with href property set display also the image.
<p><em>Attachment:</em> </p> <img src="" >or
Syntax: {{or <value 1> <value 2> … }}
Description: Evaluates logical or for two or more given arguments.
Example: Output the full user story text created from asAn, iWant and soThat custom attributes for all document objects, which are user stories or constraints.
<p> <strong>[]</strong> <em>As a(n)</em> <em>I want to</em> <em>so that</em> .</p>not
Syntax: {{not <value>}}
Description: Evaluates logical not for the given argument.
Example: Output the document object ID as the prefix of the text description for all document objects with text attribute set or without any children.
[]cond
Syntax: {{cond <test> <value 1> <value 2>}}
Description: Returns either <value 1> if <test> is truthy or <value 2> if <test> is falsy.
Example: Output the count of outlinks or inlinks based on the type attribute.
ifEqual
Syntax: {{#ifEqual <value> <value>}} … {{/ifEqual}}
Description: Compares two arguments and outputs the block only if both arguments are equal.
Example: Output document object ID only if value of type attribute equals to “Req” string:
<span></span>if and eval helpers instead.Variables
var
Syntax: {{var <varId> <value>}}
Description: Declares a variable with the given ID and sets its initial value.
Example:
set
Syntax: {{set <varId> <value>}}
Description: Sets the given variable to the given value. The value should be of the same type as the initial value.
Example: Set value of variable x to the value of custom attribute estimate:
get
Syntax: {{get <varId>}}
Description: Outputs value of the variable with the given name. The helper can also be used to retrieve array contents when using the #each block helper, see push helper for an example.
Example: Output the initial value of variable x which is 0:
<div>x=</div>incr
Syntax: {{incr <varId>}}
Description: Increments value of the given number variable.
Example: Count number of document objects in c variable:
<div><b>Count:</b> </div>decr
Syntax: {{decr <varId>}}
Description: Decrements value of the given number variable.
join
Syntax: {{join <value 1> <value 2> [<value 3> … <value N>] [separator=<string>]}}
Description: Creates a new string by concatenating all passed values, optionally separated by a specified separator string.
Example: Return myValue property with a prefix and suffix:
Example: Join values using a comma as separator:
Arrays and Maps
array
Syntax: {{array <arrayId>}}
Description: Declares an array with the given ID.
Example: Create array named x, fill it with values and then print all array values.
Example: Iterate the array of comments stored in the discussion property of the current document object and print the comment:
:Note: The Handlebars built-in block helper each sets the evaluation context to the current element of the array. However, most of ReqView custom helpers work with a specific context from the exported project, e.g. a document object. To change the evaluation context use block helper with. To declare a scoped parameter without changing context use helper let. See the following example demonstrating combined usage of helpers each, with and let.
Example: Iterate outgoing satisfaction links of the current document object and display values of all attributes defined in an array.
<ul> <li> : <em></em>: "" </li> </ul>map
Syntax: {{map <mapId>}}
Description: Declares a map (key-value store) with the given ID. Maps can also be used to emulate sets (collections of unique elements).
Example:
setElement
Syntax: {{setElement <arrayOrMapId> <element> <value>}}
Description: Sets the value of an element of an array or a map with the given name to the given value; element must be a string or a number and arrayOrMapId must be an array or map variable.
Example: Add/set the value of map x element with the key given by output of docObjId helper (e.g. "SRS-123") to the value of document object attribute text:
Note that docObjId is a template helper and must be enclosed in brackets.
Example: Add/set the element at index 0 of array x to the value of document object attribute text:
getElement
Syntax: {{getElement <arrayOrMapId> <element>}}
Description: Outputs the value of an element of an array or a map with the given name; element must be a string or a number and arrayOrMapId must be an array or map variable.
Example: Set the element of map x with key “id” to string “NEEDS-123” and then output the formatted value string:
<div>x.id=</div>Example: Set the element of array x at index 0 to string “NEEDS-123” and then output the formatted value string:
<div>x[0]=</div>deleteElement
Syntax: {{deleteElement <arrayOrMapId> <element>}}
Description: Deletes the given element of the given array or map. When used with a map, the element must be a valid key of the map. When used with an array, the element can also be negative to allow indexing from the end of the array (the last element is at index -1).
Example: Delete the element with key docObjId from map x:
Example: Delete the first element from array x:
Example: Delete the last element from array x:
push
Syntax: {{push <arrayId> <value>}}
Description: Adds the given value to the end of the given array.
Example: Output all elements of array x together with their indices:
<div>: <br /></div>pop
Syntax: {{pop <arrayId>}}
Description: Removes the last element from an array and returns that element.
Example: Remove and output the last element from array x:
Tip: To delete the last element without output, use the deleteElement helper with -1 as the element parameter.
size
Syntax: {{size <arrayOrMapId>}}
Description: Retrieves the size of the given array or map variable.
Example: Output the length of array or map x:
clear
Syntax: {{clear <arrayOrMapId>}}
Description: Clears the contents of the given array or map variable.
Example: Clear map or array x:
includes
Syntax: {{includes <name> <value>}}
Description: Checks if an array includes a value, a map has a key or if an enumeration attribute (both single- and multi-valued) value matches. The name argument must be a name of an array or a map variable, or a name of an enum attribute in the current context.
Example: Print a note if multi-valued enumeration attribute components value includes “Server” component:
Server component supportedExample: Output a warning if map verLinks does not contain an element with the key given by output of docObjId helper:
<div><b>Warning:</b> Missing verification link!</div>sort
Syntax: {{sort <arrayOrMapId> [sortByValue=<bool>] [locale=<string>]}}
Description: Returns a sorted copy of an array or map. The sorting algorithm is case-insensitive, diacritics-sensitive and sorts by numerical values of integers (decimal numbers must have fixed precision for the sorting to work). Maps are sorted by element keys unless sortByValue=true parameter is provided. Optionally, to get the correct sort order of a specific language, you can use a IETF BCP 47 language tag as the locale argument.
Example: Output sorted elements stored in array x:
<div>: <br /></div>Example: Output key-value pairs stored in map x sorted by key:
: ;Example: Output key-value pairs stored in map x sorted by value:
: ;Example: Sort array x using the Swedish locale, where “ä” sorts after “z”:
<div>: <br /></div>eachOfMap
Syntax: {{#eachOfMap <mapId>}} … {{@key}} … {{@value}} … {{/eachOfMap}}
Description: Iterates all elements of the given map in the original insertion order of the keys.
Example: Output all elements of map x in “<key>: <value>” format:
: ;Example: List 3rd level requirements (e.g. software requirements) associated with the current 1st level requirement (e.g. a stakeholder need) while preventing duplicate entries:
<div><em>:</em> </div>Note that you may need to clear the satLinks map by {{clear "satLinks"}} before it is reused in the context of another document object.
Search & Replace
searchString
Syntax: {{searchString <string> <string>}}
Description: Searches a string given by the first argument if it contains a substring given by the second argument.
Example: Returns true if text attribute of a document object contains “shall” substring:
searchRegexp
Syntax: {{searchRegexp <string> <pattern> [flags=<string>]}}
Description: Searches a string given by the first argument if it matches a regular expression pattern given by the second argument. You can optionally provide flags parameter for the regular expression.
Example: Returns true if text attribute of a document object matches “shall” keyword with ignoring case:
replaceString
Syntax: {{replaceString <string> <string> <string>}}
Description: Returns a string given by the first argument with replaced substring given by the second argument by a string given by the third argument.
Example: Output a string with replaced “shall” substring in text document object attribute by "<b>shall</b>":
<div></div>replaceRegexp
Syntax: {{replaceRegexp <string> <pattern> <string> [flags=<string>]}}
Description: Returns a string given by the first argument with pattern given by the second argument replaced by a string given by the third argument. You can optionally provide flags parameter for the regular expression.
Example: Output a string with replaced all occurrences of the keyword “shall” in text document object attribute content by "<b>shall</b>":
<div></div>Other Helpers
debug
Syntax: {{debug}}
Description: Outputs information about properties available in the current context.
Example: Output debug information about all set document object attributes (heading, text, …):
<!-- -->user
Syntax: {{#user}} … {{/user}}
Description: Outputs the name, email or company of the current user.
Example:
<a href="mailto:">, </a>repeat
Syntax: {{#repeat <number>}} … {{/repeat}}
Description: Repeats the block content a specified number of times. Provides @index, @first and @last variables.
Example: Output all array elements in reverse order:
Example: Output sequence [1, 2, …, 5] using @… variables:
[ ] , Example: Iterate across two dimensions using parent context:
X: , Y:
let
Syntax: {{#let <var 1>=<value 1> [<var 2>=<value 2> … <var N>=<value N>]}} … {{/let}}
Description: Creates scoped named parameters with custom data without changing the current context. The parameter values can then be accessed using @-prefixed names like @<var 1>. This is particularly useful for exposing data from parent contexts and for reuse of expression results.
Example: Access the source document object and document contexts and a computed value when inside the #eachLink helper:
<div>:</div> <div>Source document last change: </div> <div>Source object ID: </div> <div>Source object property A: </div> <div>Source object computed Foo: )</div> <div>Destination object ID: </div> <div>Destination object property A: )</div> Export HTML Format
HTML Tables
You can export structured ReqView documents as HTML tables displaying requirements preserving the document hierarchy in one column and custom attributes in additional columns.
Example: Export the current document to an HTML table with columns ID, Description, and Status.
<table> <thead> <tr><th>ID</th><th>Description</th><th>Status</th></tr> </thead>
<tbody> <tr> <td></td> <td> <div> <img src=""></br> <em>Image attachment:</em> <span></span> <em>File attachment:</em> <span></span> </div> </td> <td></td> </tr> </tbody></table>Example: Export the SRS document from the Example Project to an HTML file. Section headings and informative paragraphs are output as HTML text with book layout, and each list of requirements within a section is output as an HTML table with columns ID and Requirement as illustrated by the following screenshot.

This example demonstrates how to reuse code in export templates by means of Handlebars Inline Partials.
</tbody> </table>
<table> <thead><tr><th style="width:8em">ID</th><th style="width:40em">Requirement</th></tr></thead> <tbody> <tr> <td><a id="" name=""></a>.</td> <td></td> </tr>
HTML Traceability Reports
Traceability Matrix
You can easily extend HTML reports with table layout to output the requirements traceability matrix to analyze impact of changes or find which functionality is not verified by tests yet.
Example: Export the Example Project to an HTML file displaying top-down traceability coverage of the top-level stakeholder requirement (NEEDS) satisfied by functional SW requirements (SRS) and verified by test cases (TESTS) as illustrated by the following screenshot:
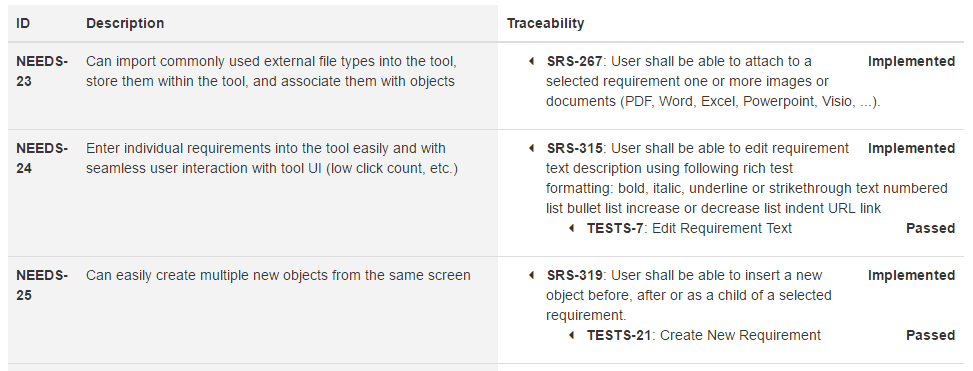
The following snippet outputs traceability links shown in the Traceability column:
<ul> <li> <span>-: </span> <span></span> <ul> <li> <span>-: </span> <span></span> </li> </ul> </li> </ul>It iterates all incoming satisfaction traceability links of the given NEEDS user story. For each such link, it renders the ID of linked SRS requirements, the short description (heading or text attributes), and the value of the status attribute.
Still in the context of the linked SRS requirement, the snippet iterates all incoming verification links. It renders the ID of linked tests, the short description, and the value of the status attribute.
Download the export template: NEEDSTraceabilityTemplate.html and try it.
Example: Export a template column Aggregated Tests listing all unique verification inlinks in a (sub)section aggregated from all descendant document objects as illustrated by the following screenshot.
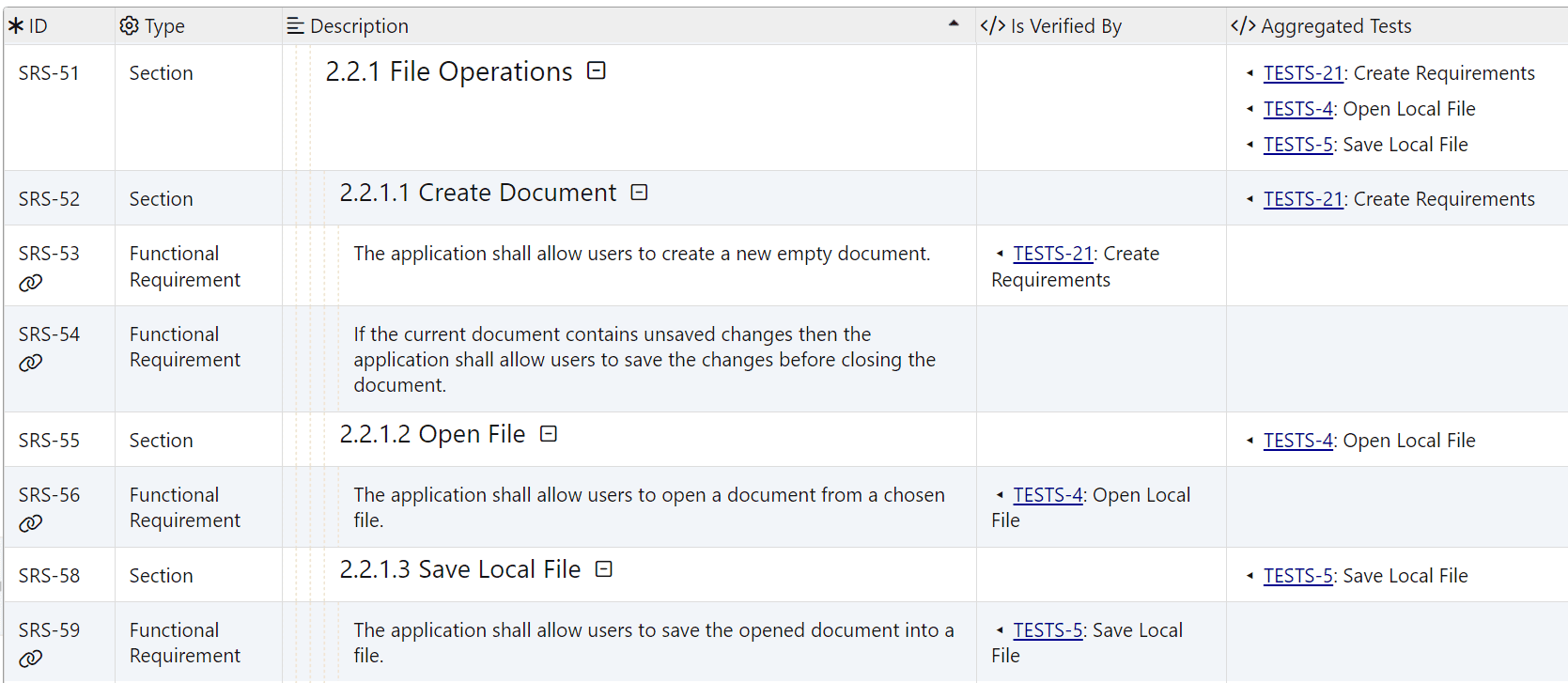
The template column uses Handlebars Inline Partials to output verification links recursively.
<p>◂ : </p>
Example: Export the document NEEDS from the Example Project as an HTML table displaying the requirements traceability matrix. The table has two columns ID and Links and contains a row for each top-level stakeholder requirement in the NEEDS document. The column Links displays SW requirements from the SRS document satisfying the stakeholder requirements.
<ul> <li>
</li> </ul>
<table> <thead> <tr><th>ID</th><th>Links</th></tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> </tbody></table>This example demonstrates how to use Handlebars Inline Partials to output traceability coverage recursively.
Example: Export selected SW requirements from the SRS document in the Example Project to HTML table displaying their detailed context in the V-model as illustrated by the following screenshot for SW requirement SRS-53.
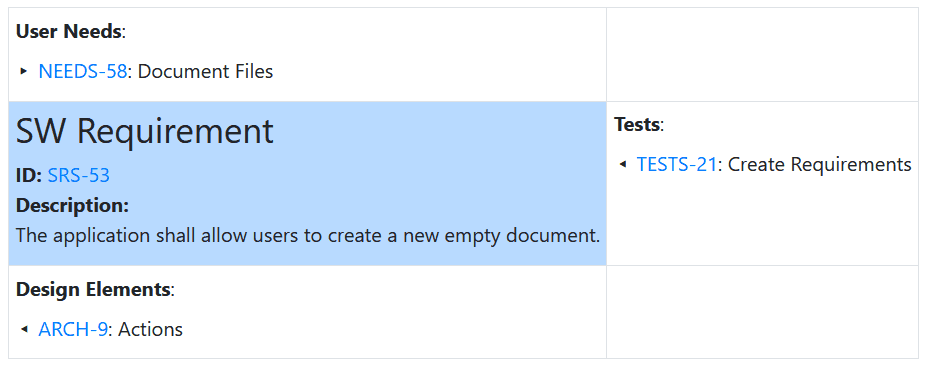
<table> <tbody> <tr> <td> <p><strong>User Needs</strong>:</p> <p>: </p> </td> </tr> <tr> <td class="table-primary"> <h3>SW Requirement</h3> <p><strong>ID:</strong> </p> <p><strong>Description:</strong> </p> </td> <td> <p><strong>Tests</strong>:</p> <p>: </p> </td> </tr><tr> <td> <p><strong>Design Elements</strong>:</p> <p>: </p> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table>Traceability Graph
You can export dynamic HTML reports using a 3rd party JS library to create traceability graphs dynamically.
Example: Export the document NEEDS from the Example Project to a dynamic HTML traceability report displaying a downstream traceability coverage graph for each user story as illustrated by the following screenshot.
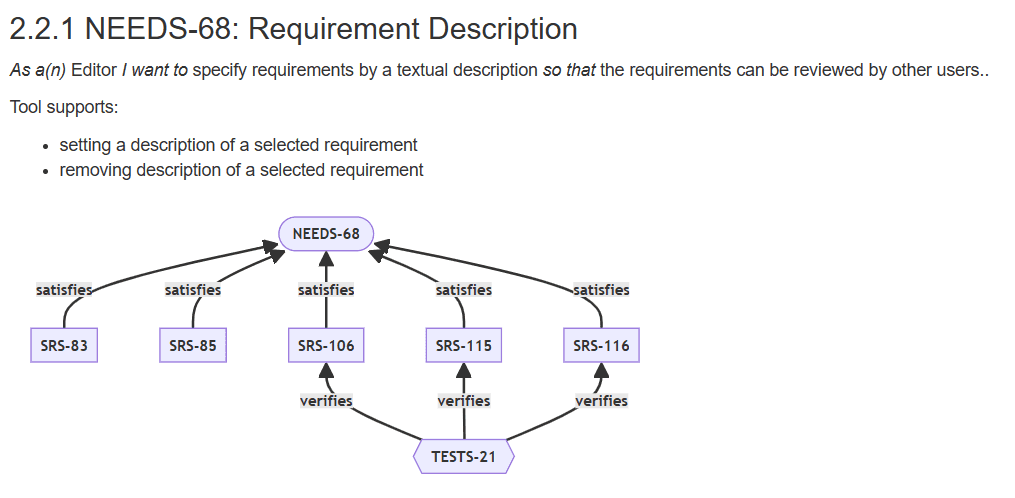
The following snippet uses Mermaid JS library to dynamically generate traceability graphs from pre HTML tags exported by the export template.
<script type="module"> import mermaid from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid@10/dist/mermaid.esm.min.mjs"; mermaid.initialize({ startOnLoad: true, securityLevel: "loose" });</script>
: <pre class="mermaid"> flowchart BT
([ ]) click "reqview:open?projectId=#"
[ ] -- satisfies --> click "reqview:open?projectId=#"
\ }} -- verifies --> click "reqview:open?projectId=#"
</pre> Download the export template: NEEDSMermaidFlowchartTemplate.html and try it.
HTML Progress Reports
You can export HTML reports visualizing project progress using a 3rd party CSS library.
Example: Export the document NEEDS from the Example Project to an HTML report displaying the status of user stories as progress bars. The report aggregates the status from children user stories for each document section, see the following screenshot.
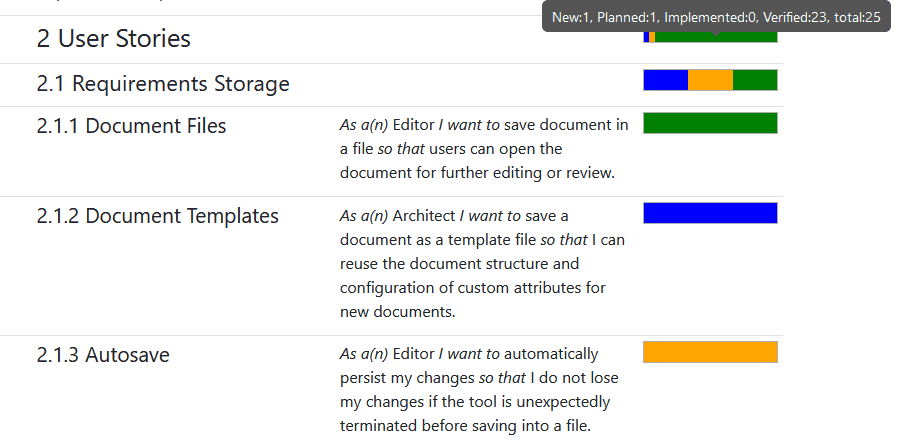
The export template is based on the predefined template HTML / Modern Report and uses the CSS library Charts.css to visualize progress bars.
The template iterates the document, recursively aggregates values of the status attribute for each child object using the Handlebars partial function statusTypesSumRecursive storing the result in the map statusTypesSum. Then the template calculates progress aggregated in the map statusTypesSum as percentages and outputs an embedded HTML table with percentage values. The table has CSS class charts-css bar multiple stacked used by the CSS library to visualize the table as a progress bar.
<head>...<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/charts.css/dist/charts.min.css">...<style>... #status-chart { width: auto; border: 1px solid #aeaeae; opacity: 0.75; }...</style></head><body>
... ...
<td>
<div id="status-chart"> <table class="charts-css bar multiple stacked hide-data"> <tbody> <tr> <td style="--size: ; --color: "> <span class="data"></span> <span class="tooltip"></span> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> </td> ...Download the export template: HTMLReportProgressBarTemplate.html and try it.
HTML for DOCX Export
You can export ReqView documents to a DOCX file with custom layout described by custom a HTML template, see Export Documents to DOCX. Exported HTML tags are mapped to Word styles as follows:
- Block elements
<h1>,<h2>, ...,<h6>tags toHeading 1,Heading 2, ...,Heading 6section headings<p>tags toNormalparagraphs<ul>tags to bullet lists<ol>tags to numbered lists<img>tags to images<table>,<tr>, and<td>tags to tables, rows and cells
- Inline elements
<strong>to bold text style<em>to italic text style<a>to URL links
Note: HTML tags should have minimum CSS styling because of known limitations of MS Word, see MSDN article Word 2007 HTML and CSS Rendering Capabilities in Outlook 2007. To customize styling in HTML templates, use HTML class attributes with a name matching word styles.
Paragraph Styles
Example: Export the current document to MS Word HTML with book layout containing system attributes id, heading, text, attachments, and displayed custom attributes. Use HTML class attributes rv-id, rv-text, rv-attachment, etc., matching Word styles defined in the default MS Word template.
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en-US"><head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title></head><body> <a name="" id=""></a> <span class="rv-id">[]</span> <p class="rv-attachment"> <span class="rv-attachment-info">Attachment:</span> <a href=""></a> <br><img src="" > </p> <div class="rv-attribute"> <span class="rv-attribute-value">:</span> </div> </div></body>Table Styles
You can customize several styling options for tables exported to MS Word, such as table spacing and borders, column widths, etc.
Example: Export MS Word table with vertical text in table header for all columns except from the Type and Description columns as illustrated by the following screenshot.

The following template snippet exports the rotated table header. It uses MS Office specific CSS style mso-rotate because MS Word ignores commonly used text-orientation and transform CSS styles for td HTML tags.
<tr> <td style="vertical-align: text-bottom;"> <td style="mso-rotate:90;height:6em"></td></td>Example: Export documents NEEDS and SRS to MS Word using table layout with column widths specified in a custom export parameters JSON file:
{ "NEEDS": { "Description": "40em", "Type" : "30em", "Story": "60em" }, "SRS": { "ID": "33%", "Description": "34%", "Links": "33%" }}The following template snippet uses the exportParam helper to read column widths from the JSON file.
<th style="width:"> </th>Images
To scale size of image attachments, use export helper imageSize in your custom HTML template, see the previous section Paragraph Styles for an example. Note that images should have fixed size because Word HTML does not support flexible image sizes based on page layout.
Word Macros
You can run a Word macro to create a list of figures containing all image attachments in the exported documents. For more information see Export Documents to DOCX > MS Word Template > Word Macros.
Export CSV Format
You can export the current document to a CSV file with columns containing information about internal and custom attributes, section level and number, and all outgoing links, see Export Requirements to CSV.
You use export templates to define the content of exported CSV files. For instance, you can export a subset of attributes, such as id and status to update status of test cases in an external tool and import changes back, see Import and Update Requirements From MS Excel > Roundtrip Synchronization. Or, you can export column with attribute id and second column with list of verification links to output traceability matrix.
Note: Use tildes (“~”) to trim whitespaces in order to not break CSV format, see Handlebars: Whitespace Control.
Example: Export CSV files with columns id, heading, text, and status storing values of the corresponding document object attributes.
"id""heading""text""status" }} }} }} }Example: Export CSV files with columns id storing the test ID and verification storing a list of verification links to requirements.
"id""verification"} Export JSON Format
Example: Export JSON files storing a list of objects with properties set to id, section, heading, and text attributes values.
[ { "id": , "section": , "heading": , "text": }]Export XML Format
Example: Export XML files structured follows:
<doc id="D"> <section id="1" title="Heading 1"> <section id="1.1" title="Heading 2"> <clause text="Text 1"/> <clause text="Text 2"/> </section> <section id="1.2" title="Heading 3"/> <section id="1.3" title="Heading 4"/> <clause text="Text 3"/> </section> <section id="2" title="Heading 5"/> ...</doc>The following snippet uses helper array as a stack to ensure that all tags are closed correctly.
<doc id=""> <section id="" title=""> <clause text=""/> </doc>Note: You can format XML files during post-processing to improve their readability.
Download Export Templates
Predefined HTML Templates:
You can download and reuse predefined templates for Export Documents to HTML:
- HTML / Modern Report — export an interactive HTML file with a table layout using modern CSS styles
- HTML / Book — export a filtered HTML file with a single column layout and minimal CSS styles, which is suitable for import into MS Word
- HTML / Table — export a filtered HTML file with a table layout and minimal CSS styles, which is suitable for import into MS Word
Predefined PDF Templates:
You can download and reuse predefined templates for Export Documents to PDF:
- PDF / Book — export a filtered HTML file with a single column and minimal CSS styles, which is suitable for conversion into a paged PDF document
Example Traceability Templates:
You can download and reuse custom export templates for traceability reports designed for the Example Project:
- NEEDSTraceabilityTemplate.html — export the top level NEEDS document to a HTML file displaying downstream traceability coverage (NEEDS ← SRS ← TESTS)
- NEEDSMermaidFlowchartTemplate.html - export top level NEEDS document to a HTML file displaying downstream traceability coverage with generated diagrams using Mermaid JS library.
- SRSTraceabilityTemplate.html — export the SRS document to a HTML file displaying upstream satisfaction links (NEEDS ← SRS ) and verification links (SRS ← TESTS)
- CSVTraceabilityTemplate.csv — export a document to a CSV file listing all document object with their reference links
- JSONTraceabilityTemplate.json — export a document to a JSON file listing its document objects with their incoming satisfaction links
Other HTML Templates:
You can download and reuse custom export templates for specific reports designed for the Example Project:
- HTMLReportProgressBarTemplate.html - export the top level NEEDS document to a HTML file displaying status attribute as progress bar.